History
Sigmund Freud, a trained neurologist popularly known as the father of psychoanalysis. Born into a poor family, his parent’s priorities were his education and were qualified as a doctor from the University of Vienna.

Source: pathdoc/Adobe Stock
He developed several theories on unconscious mind and found psychoanalysis a treatment for psychopathology. The psychoanalyst will communicate with the unconscious mind of the patient which was later developed into many areas of psychotherapy.
Through this analysis a person’s behavior can be evaluated relating to the previous life experiences or traumas. These experiences characterise one’s behavior.
And also one of the other prominent discoveries of Freud was the dream psychology, where the dreams generate sensory stimuli which is been appeared as his fulfilled wishes in order to sustain his sleep.
These theories are considered to be the biggest contributions to the century and have inspired the development of many communication theories and models.
Introduction
A crucial factor for every human being is achieved through proper communication or through social interaction. Apart from the basic essentials, a person’s needs lies in their desires. In other words wish fulfillment which can be categorized as the basic need to be loved or to be understood.
These desires can be generated consciously or unconsciously and people often tend to confuse it and rather reach to a stage where they fail to identify their needs and wants.
Psychoanalytic theories are a complex set of theories and principles to understand and to study the human behavior, personality, logic and thoughts of a person.
Sigmund Freud is the pioneer in developing these theories followed by many psychologists like Erik Erikson. The theories are vast and are unpredictable at times as the behavior of a human mind.
Psychoanalytic Theory
Human behavior is not something inborn but is shaped by the experiences that a human being encounters throughout his life. We tend to deal with a situation consciously but will be driven by our unconscious intuitions.
For example we always feel weird or awkward after doing or telling something to another person. We might not think about it during the situation, but afterwards only our mind comes in conscious of what we had done.
Basic Concepts of Mind is divided into three sections:
- Conscious mind is the feelings and desires that you feel at present.
- Preconscious is the memory or any event that you find it easy to recollect and also the humanitarian part.
- Unconscious which is the vast area which will be difficult to recollect but these will be memories caused by the experiences of our conscious behavior.
During 1923 Sigmund Freud divided the mind into three stages is called “Personality Structure”.
- ID (“eedh”)
- Ego
- Super Ego
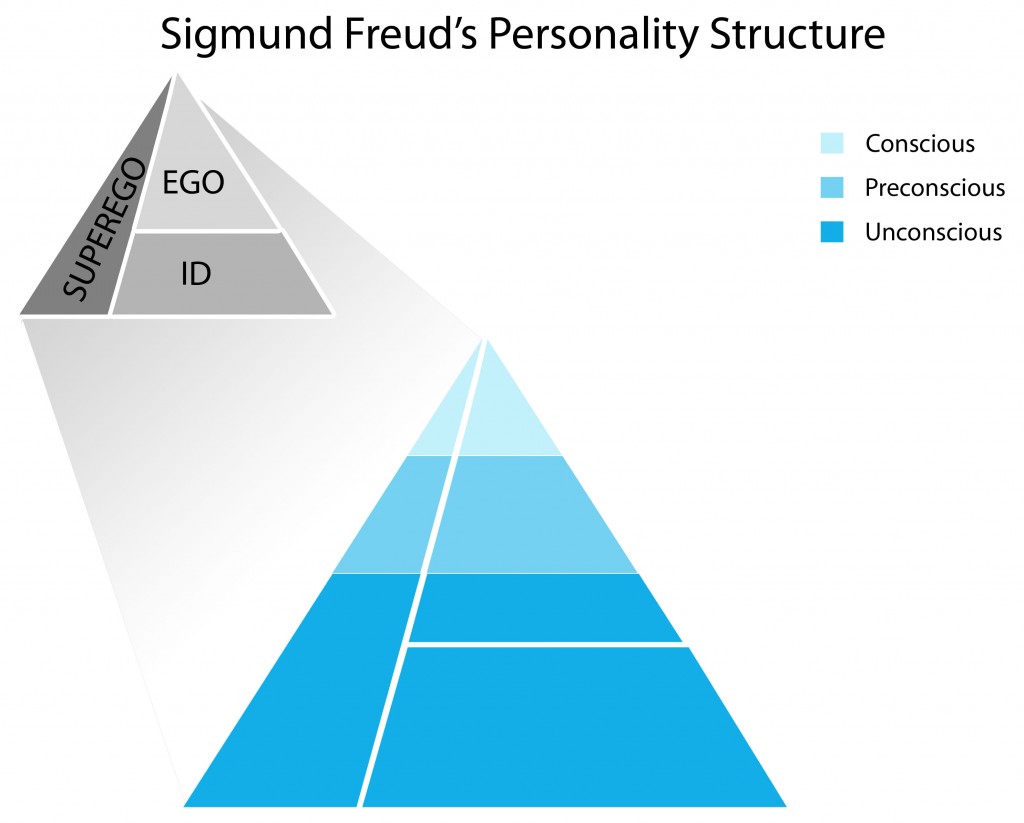
1. Id is the first stage, the human wants to fulfill their desire (demand) whether it is right or wrong. Individual seeks for pleasure and to avoid the pain. There is no moral values or standards in this stage. It’s unconscious mind.
Example: The child never stops crying until the mother fulfills the desire of the kid. (Kid fighting for Ice cream)
2. Ego is the second stage which is the balance between both id and superego on one hand & reality on another hand. In this stage individual demands as well as obey for the reality principle (real life). It’s stands in between both conscious and preconscious.
Example: In the University campus, Students are protesting or demanding for their scholarship in a democratic way.
3. Super Ego is the third stage which is entirely opposite to the Id. In the stage the individual concerned with moral values, emotions, expectation, standards and ideals. It is mostly unconscious and some part is preconscious.
Example: A good politician has several ways to involve in scam. Even though, he will not do that because of his ethical and moral values won’t allow.
Related: Defense Mechanisms
Scope
The psychoanalytical theory was greatly influenced in the interpersonal communication and provided a technique for understanding and interpreting human thoughts and behaviors and also the past events reshaping our personality. This approach provides a vast possibility in the field of communication as it explains how human beings react contrary towards similar situations.
Example
When two people are conversing, their attitude towards the situation comes out of not just consciously, but a clash of our preconscious and unconscious minds.
If the person whom we are talking to is agonizing, a small thought inside will sometimes cause you to yell or scream at him. But our preconscious part influences our mind and thus we tend to listen to him uncomplainingly.
The events that are stored in our unconscious minds mostly reshape our behavior naively. Examples of such events can be any trauma’s happened in childhood or some events which have caused an effect like any sexual abuse or sudden death of closed ones.
I like this blog so much, saved to fav.
Thank you.