George is a 9-year-old child. He spots a lighter on a table and attempts to play with it. A hint of fire comes out and touches his finger. He feels the pain and learns that fire is dangerous, and that lighters are not meant to be played with. This incident or experience teaches him something.
Experiential learning states that individuals learn by doing. We learn through experiencing an incident, situation, feeling or event. It is based on the idea that the best way to learn something is to experience it. These experiences or situations help us formulate the concept and remember it for a longer amount of time.
History
In 1984, David Kolb introduced experiential learning theory. He was inspired by the work of Jean Piaget, Kurt Lewin, and John Dewey. His model gained recognition and he is now best known for giving this theory. He gave a 4-stage cycle of learning and 4 separate learning styles.
Kolb’s Learning Cycle
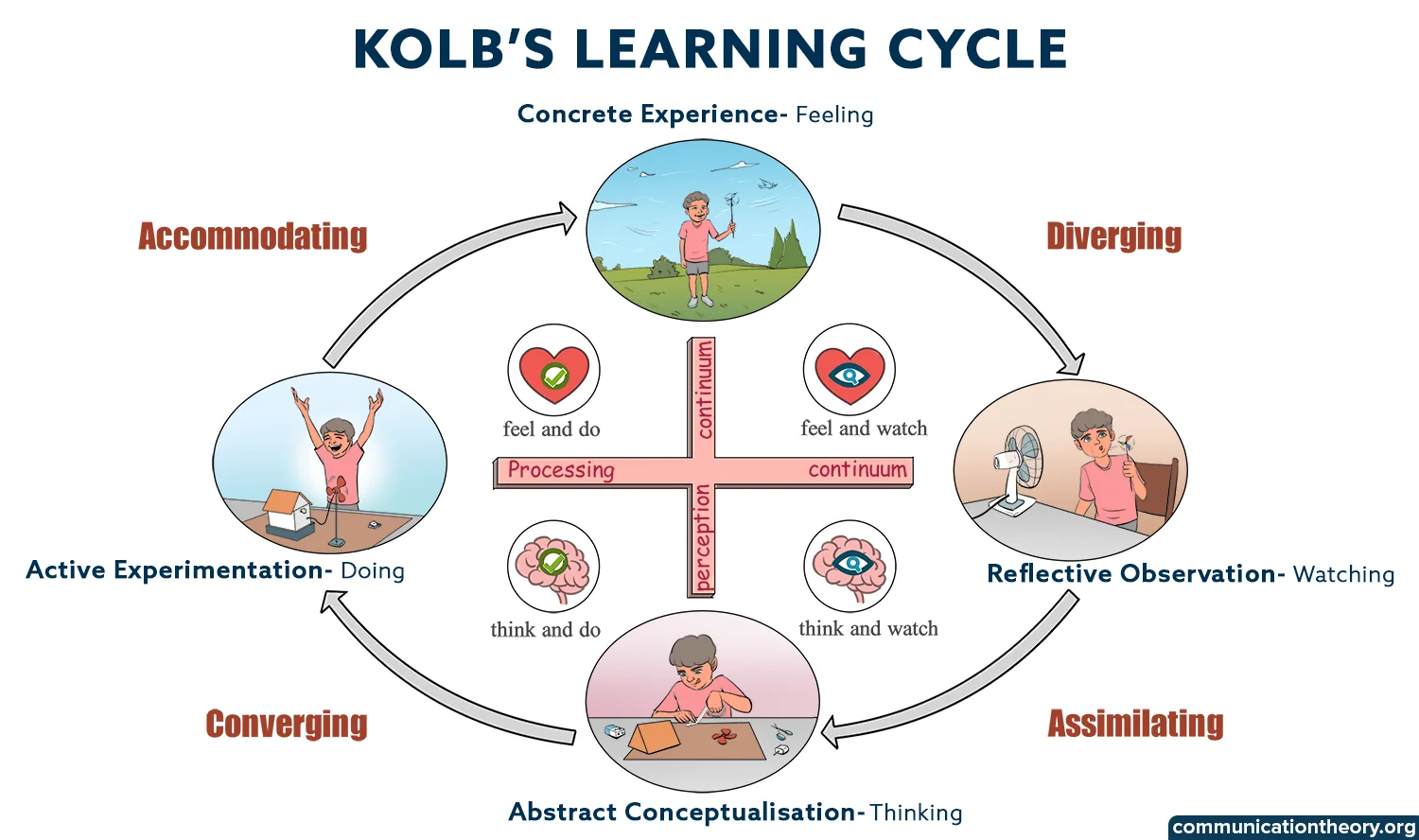
Kolb gave this learning model or cycle to understand the process of learning. According to him, concrete learning and abstract conceptualization are about ‘grasping experiences and reflective observation and active experimentation are about ‘transforming experiences.’
Grasping experiences are defined as actions that are done or watched by an individual. Here, concrete learning and abstract conceptualization include watching and doing.
Transforming experiences are defined as things that can be thought or felt. Here, it includes thinking or feeling about an event or person. Reflective observation and Active experimentation include the thinking and feeling components.
Concrete Learning
This learning is the first step or stage. It occurs when an individual experiences a new event or looks at a past event in a new way.
For example, watching a bird fly for the first time or reading a book from a relatively new genre.
Reflective Observation
This is the second step or stage of learning. In this stage, the individual reflects on the experience or event personally. They interpret and reflect on the experience based on their characteristics.
For example, watching a movie and relating to a character personally.
Abstract Conceptualization
This is the third step or stage. In this stage, the individual adjusts or adapts their thoughts or thinking based on the experience they had and their interpretation and reflection on it. They might develop new thoughts or feelings based on this new experience.
For example, adapting their thoughts and interpreting events in their life according to the new reflection found through a real-life based documentary.
Active Experimentation
This is the last step of the cycle, and it includes applying new ideas or modifying previous ideas based on the new experience they had. This stage can be achieved in a short period or a long span of time.
For example, applying tips or ideas from a cooking workshop in real life.
Learning occurs when an individual passes through all stages. He or she experiences a new event, leading to reflection and interpretation of that event, forming some conclusion, assumption, or generalization from this event, and then testing this conclusion or assumption by applying it in the real world.
Kolb stated that the learning stages lead to one another and one can enter any stage and the sequence is followed. Most effective learning occurs when all stages are experienced sequentially.
Related: Constructivism
Factors Required For Learning
According to Kolb, there are a few factors that are required to ensure effective learning through experience:
- A willingness to be actively engaged in a particular experience.
- An ability to reflect on the experience.
- An ability to interpret and logically understand the experience through analytical skills.
- An ability to use the new information learnt through the experience by taking appropriate decisions and forming relevant opinions or generalizations.
Kolb’s Learning Styles
Kolb believed that different people have different learning tendencies. Everyone might use all types of learning in their life, but one style or type is dominant for each and every one. He gave 4 different learning styles, based on the 4-step learning cycle. These styles are explained below.
1. Diverging
This learning style includes observing and reflecting on a situation before taking any action. Divergent learners tend to look at things from a different perspective and then act. They believe in watching or observing before doing.
They have vibrant imaginations and are often team workers. This style was known as ‘diverging’ because this style included generating multiple ideas, and people from this style tend to like knowing about different cultures and traditions and are open to different perspectives.
In a classroom, this could look like an exploration of a particular chapter, multiple resources for gaining information and focusing on all aspects of the topic while teaching. Students can also engage in brainstorming or working in groups to present a topic to the class.
2. Converging
This learning style includes solving issues or problems by applying learnt knowledge or skills. Convergent learners can execute tasks by using previous knowledge and experiences. They can do practical and technical tasks with ease. They are not very inclined towards social or interpersonal issues or approaches.
They believe in experimenting and doing things. In a classroom, this would look like distributing worksheets and asking the students to solve problems in class or work on computer skills.
For example, using previous knowledge about addition and subtraction to solve multiplication and division problems.
3. Assimilating
This learning style includes using a logical and analytical approach to solve problems or reach conclusions. Learners prefer this style to use theories and logic rather than practicality to understand concepts. They believe in organizing information in logical format and sequences. They thrive on logical, coherent explanations rather than practical examples for learning concepts.
They would prefer reading theories and research papers to actual experimentation. People with science and math interests could prefer this learning style. In a classroom, this would look like giving students a project to work on by themselves, which would require them to use logical reasoning.
For example, solving sudoku or puzzles that require logical thinking and reasoning.
4. Accommodating
This learning style involves using practicality to solve problems and reach conclusions. Concrete learning or experiences as well as active experiments are used to come up with solutions. Learners of this type enjoy new challenges and tasks and often use intuition to come to conclusions.
They believe in their own ‘gut’ feelings as well as rely on other people’s judgements while forming conclusions or forming opinions. This style is used by almost everyone in daily, regular contexts. In a classroom, this could look like deeper class discussions and engaging activities.
For example, using ‘guts’ to come to conclusions about another person’s behavior.
Applications In Education
This learning theory can be used in educational institutes to facilitate and encourage learning in different subjects. For instance, teachers can ensure that there are multiple modalities for learning a single concept, for every type of learner in a class.
Teachers can use more practical examples to ensure experiential learning, as it holds more attention and lasts longer in memory. Students can be tested and made aware of their specific learning styles so that they can learn better, and hence, perform better.
Teachers can use science projects or experiments, art projects, field trips, role-playing, interactive or collaborative games and assignments to teach subjects and topics.
Benefits Of Experiential Learning
An individual can experience real-world issues through experiential learning. They can experience what it would be like to work in a particular field, by having an internship experience in that area. Their overall performance in a particular area could be better if they learnt something in that area through previous experience. That experience could lead to a boost in their current performance.
They could come up with creative, unique solutions if they have experienced experiential learning in the form of projects or art assignments. This type of learning requires trial and error. Children or individuals can make mistakes while learning a particular concept before applying the concept in the real world. Hence, experiential learning provides opportunities to make mistakes, reflect, get creative, and prepare for real-world problems.
For example, observing the birds, animals and/or others by visiting a zoo, or on a jungle safari and learning about them. Other examples include learning in an internship, making mistakes and growing along the way and then joining a full-time job in the same field. Previous experiential learning experience would be helpful in the job.
Criticism Of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning does not account for people who do not reflect on their experiences. It also does not account for learning in larger groups of people. It does explain learning stages in individuals but does not emphasize learning in social groups. The theory has been described as narrow and restrictive by some critics as some learning styles tend to change over time and no explanation has been provided for the same.