During the 1960s when practitioners conducted a long and exhausting therapy sessions with clients, assessing their repressed sexual needs, Aaron Beck proposed a therapy technique called Cognitive Behavior Therapy (shortly known as CBT), which was considered as a breakthrough in the field of Psychology.
Today, one of the most effective and commonly practiced therapy techniques employed by therapists throughout the world is CBT, which is backed up by a consistent number of empirical evidence supporting its efficiency time and again.
Basic Assumptions Of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is a therapy technique which views mental illness from a cognitive and behavioral perspective. It adopts a problem focused approach to treatment. Beck theorized that thoughts, feelings and behaviors interchangeably affect one another. People with depression engage in a distorted type of thought pattern called cognitive distortions which contributes to a negative belief about various aspects of their lives.
During therapy, Cognitive therapists work toward challenging the distorted thought pattern in clients to help them acquire insight into their thought fallacies. Therapists use various techniques such as cognitive thought journal, relaxation methods, exposure therapy, systematic desensitization, cognitive restructuring etc. to help clients overcome the flooding of negative thoughts and replace them with positive beliefs, thoughts and behaviors.
What are Cognitive Distortions ?
Aaron Beck in the 1960s proposed that humans fall into mental disorders such as depression and anxiety because of what he termed “cognitive distortions” that distort the healthy thinking pattern and make one susceptible to various mental issues.
Cognitive distortions are faulty thinking patterns or flaws in perspective- taking or irrational beliefs, which distort reality and present themselves in a negative light which humans perceive as true and lead their lives around those beliefs.
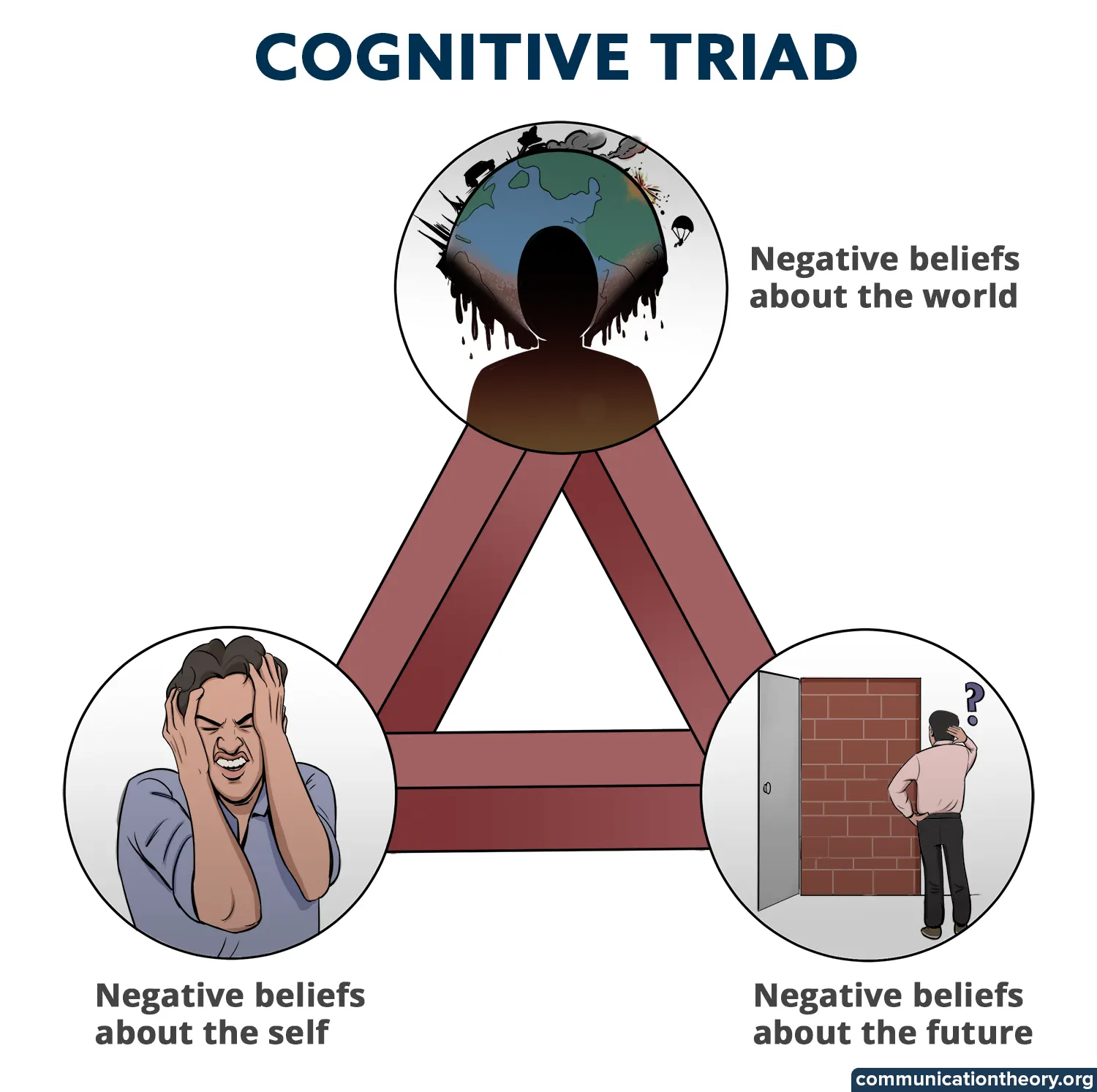
Beck believed that when a person is suffering from depression, the stressors activate the negative automated thoughts (NAT) which get manifested into acquiring negative beliefs about three aspects of their life, which he termed “The negative cognitive triad”.
The negative cognitive triad consists of negative beliefs about the self, the world and the future. Humans distort their cognitions around these three aspects.
For example, Jennifer believed that she was nothing, but a total mess and that this world is a horrible place and her future seems gloomy.
What are the Different Types of Cognitive Distortions ?
Beck has conceptualized that there are many kinds of distortions that people engage in. These distortions serve as the guide to lead lives a certain way, in most cases in a self-handicapping way and they are:
1. Overgeneralization: When a person makes a generalized assumption about something based on a few random instances.
For example, when Tina’s teacher punished her, she believed that all teachers punish students.
2. Catastrophizing: This is when a small or minor incident is blown way out of its proportion or when something is being extensively exaggerated.
For example, Jeffrey believed that if he failed any of his exams that his life is over and there is nothing else to look forward to.
3. All or nothing: This is the type of cognitive distortion where a person thinks in polar extremes. Like the famous saying goes “my way or the highway”, this person either places themselves on a pedestal or dumps in the garbage.
For example, Roger thinks he is a pro at archery right after making his first shot. When he tried for the second time and the bow went flying, he believed that he was a complete failure.
4. Filtering: A person only chooses to look at everything in a negative light and filter out the positive evidence surrounding them.
For example, Christina wants to end her marriage with her husband because he doesn’t come home early. But she ignored the fact that he helps her with the household chores and puts the baby to sleep after he comes home from work and also makes sure to spend the weekends with family.
5. Mind reading: This is when a person makes assumptions about others’ perceptions, thoughts, behaviors and attitudes without any base or solid evidence to defend their beliefs.
For example, Carla believed that her friend didn’t show up at her place because she doesn’t want to spend time with her.
6. Personalization: Taking every small instance at a personal level and holding a belief that everything said or done has to do with them.
For example, when Angela saw both her friends talking, she was sure that it was gossip about her.
7. Arbitrary inference: Reaching conclusions with little or no evidence to support their beliefs. Here, people make concrete conclusions purely based on the assumptions they make and what they believe perfectly fits the puzzle.
For example, Ronald reported to the police that the hooded man walking past him on the street was the suspect of theft, as his demeanor matched that of a thief.
8. Emotional belief: To believe that when a person feels a certain way, their feelings have to be valid or reliable although they may not be backed up by sound evidence.
For example, Sheila frequently felt that her husband was seeing someone else and she chose to believe her feelings and fight with him about it rather than investigating if her feelings could be true or not.
9. Fortune telling: Making bold predictions holding little to no evidence.
For example, Stacy believed that she would never become the fashion designer that she aspired to become.
10. Labeling: This cognitive distortion is very similar to that of overgeneralization but at a much more extreme level. Here, a person makes assumptions about themselves, something or someone based on just a small instance or experience.
For example, when Martha was mugged by an African, she became wary of them and strongly assumed that every African is a criminal yet to harm her.
Strategies To Overcome Negative Bias or Distortional Thinking Pattern
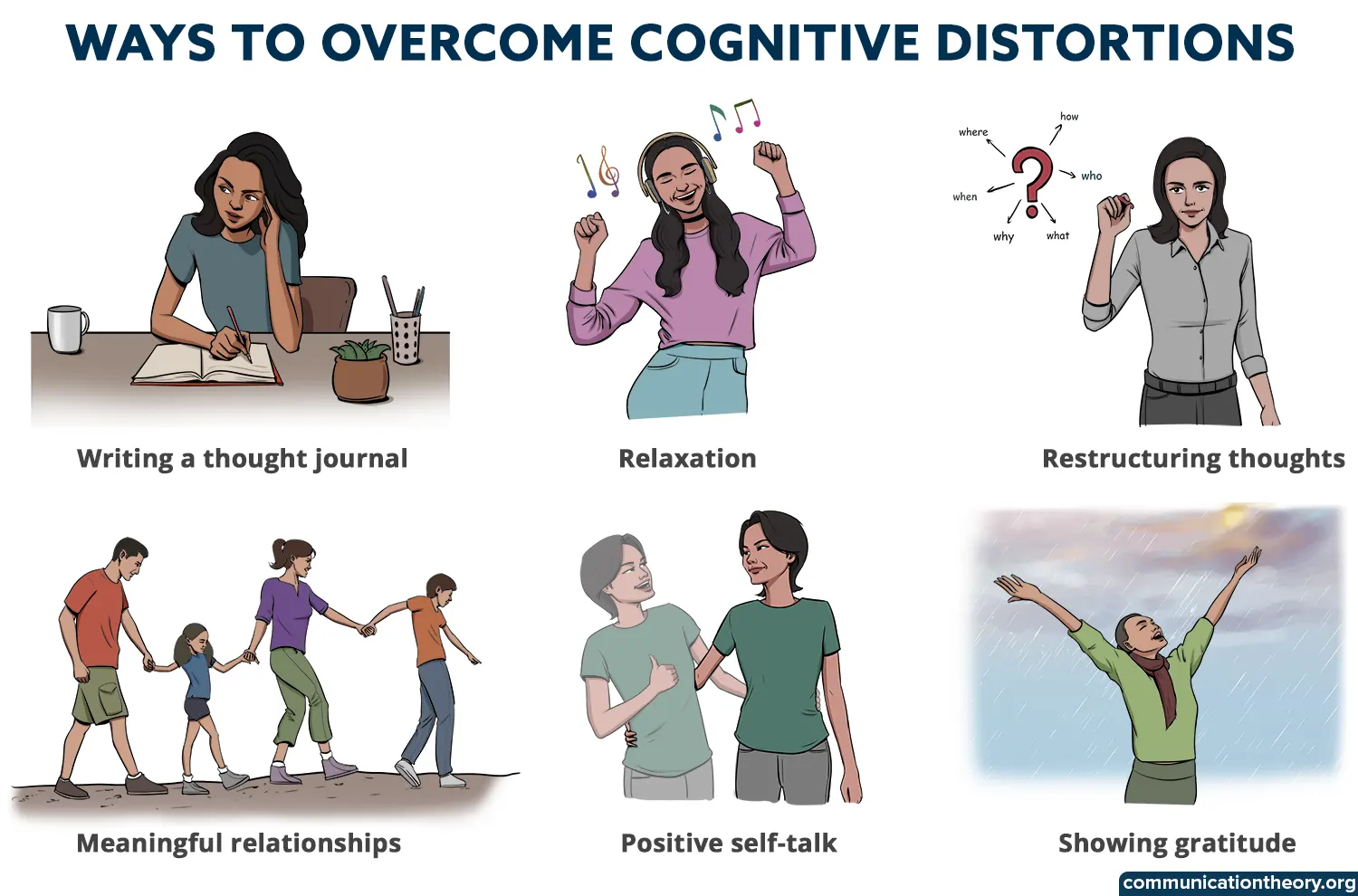
- Cognitive thought journal or thought record: This is a systematic method of monitoring one’s negative thought pattern. In this method, the triggers that elicit a specific negative behavior, thoughts or feelings are noted down which is followed by an alternative thought which can be used instead of the non-serving thought pattern. For example, instead of thinking “I’m never going to get better at this”, a better alternative statement would be “I may fail but I will get better at it with practice”.
- Relaxation method: This is a proven method to calm one’s racing mind and identify the nature of thoughts one possesses. This method involves sitting in a relaxed posture and placing one’s focus on the breathing pattern, the internal and external sensations, the environment, the tension and the relaxation of body muscles etc. this method is specifically proven effective for anxiety and depression.
- Cognitive restructuring: When a negative thought arises, asking questions such as “Do I have enough evidence to prove this thought true?” can help one identify how realistic or distorted the thought pattern is.
- Positive affirmations: Writing down or orally saying statements such as “I am worthy”, “I am strong and capable” etc. can help counteract the negative beliefs one may have about themselves, the world and the future. Many studies have proved that positive affirmations strengthen the neural pathways that are associated with self-image.
Strategies To Cultivate Optimism And Positive Attitude
- Gratitude journal: Gratitude journaling is said to be effective in sowing optimism and positivity. Creating a productive habit of writing down three things that one feels immensely grateful for, can be a great start to living a contented life.
- Mindfulness meditation: This is a great way to unwind and lead a stress-free life. Taking a few minutes out to focus on the inner self and letting the thoughts flow can be efficient in understanding oneself for who they are, inclusive of their strengths and weaknesses.
- Meaningful relationships: Humans are social beings and hence building a solid network of people can make life happy and meaningful. Engaging in heartfelt deep conversations with friends and family can bring in a sense of belongingness and add more value to life.
- Building hobbies: It is essential to nurture our interests and preferences. Hence, taking out time for oneself from the daily grind and engaging in activities that one intrinsically enjoys can enhance one’s creativity and help keep one’s spark alive.
- Positive self-talk: Always addressing oneself with love and kindness, using positive statements in the place of negative ones and surrounding oneself with such words helps to bring in acceptance and self-love.