Abraham Maslow in 1943, developed a hierarchy of needs that explains motivation fruitfully in a paper titled ‘A Theory of Human Motivation’. Later, he published a book named ‘Motivation and Personality’, and mentioned multiple needs be important for humans to be motivated. This was named after him as, Maslow’s hierarchy of needs for motivation.
Motivation is the term used to describe a need or desire that stimulates and drives behaviour. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is one of the famous theories that gives explanations on how we get motivated to do things.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs – Explanation
According to Maslow, each person had a different set of needs at different point of time in his life. He said that all needs of humans could be arranged in a hierarchy. Each person is said to move through the hierarchy by fulfilling each level of needs. Some people may have dominant needs at a particular level and thus never move through the entire hierarchy.
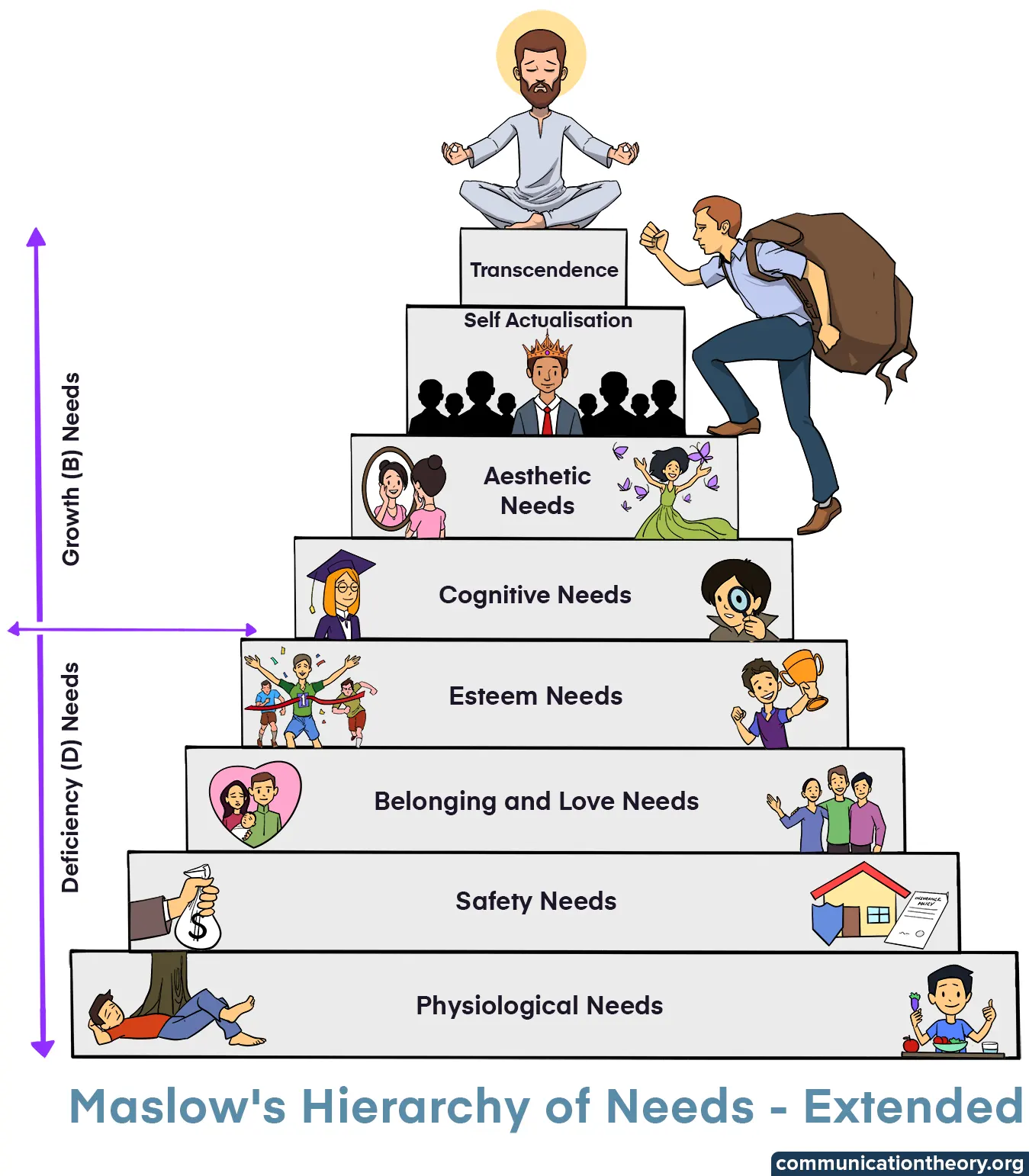
The levels are presented in the form of a triangle or a pyramid with the largest and most fundamental levels of needs at the bottom tier, and the need for self-actualization at the top. According to Maslow physiological, security, social, and esteem needs are deficiency needs or D-needs that arise because of deprivation. The highest-level of the pyramid is called the growth needs or B-needs.
Maslow also mentioned that we may meet 2 or more needs simultaneously. For example, if a person needs financial support, he can ask his family or friends for help. In this way, his belongingness and safety needs are met at the same time.
The various needs explained in Maslow’s hierarchy of needs can be subjective, but the order is not necessarily fixed. For example, people work for long hours without having their physiological needs (food or water) met completely.
Physiological needs: These are the basic biological needs such as hunger and thirst. These needs lie at the bottom of the pyramid. These needs are essential for survival. For example, air, warmth, water, food, shelter, and sleep. If these needs are not met, humans have the potential to get sick and in extreme circumstances, die.
Safety needs: They are the need to be physically safe and sound. They come just above physiological needs. For example, political safety, insurance policies, safety at the workplace. If these needs are fulfilled appropriately, an individual can feel safe and secure in their world. If these needs are not met, it could lead to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other mental health imbalances. An individual could also be physically unsafe if these needs are not being appropriately fulfilled.
Belongingness and love need: They are the need to give and receive love and to be accepted. They come after safety needs. For example, friendships, family, relationships with colleagues, social groups. These needs can be gratified with college reunions, family get-togethers, picnics, date nights or being part of a social group. This need is helpful in times of stress and pressure.
For example, Reya is living apart from her family due to a change in her workplace. She used to feel lonely before. She has now formed a group with people from her workplace, which helps her feel better than before. If these needs are not met appropriately, an individual might get depressed or anxious. He or she could face loneliness and imbalanced mental health.
Esteem needs: They are the need for competence and achievement. They come after belongingness and love needs. For example, rewards, awards, certificates, promotions, honourable mentions. It is important to be and feel respected by our colleagues, friends and family. Maslow revealed that others’ respect and admiration is a lower-level esteem need and the respect we have for ourselves is a higher-level esteem need. It is termed higher level because you are the only constant in your life at all times, so self-respect is important to survive comfortably. If these needs are not met, an individual might feel worthless and under-appreciated and could go through feelings of sadness because of it.
Self-actualization needs: They are the need to realize one’s full potential. It is at the top of the pyramid of the hierarchy of needs and not everyone can reach it. Maslow believed that this need would arise when all other lower-level needs are met.
It basically refers to doing something that we are meant to do. It could be about uplifting others or achieving something huge by yourself. According to Maslow, people who have reached this need are creative and show self-acceptance. He performed experiments on the case studies of people and their life history who he found to be self-actualizing. He then stated some common characteristics of self-actualizing people. Maslow mentioned Abraham Lincoln, Mother Teresa, etc. to have reached that level.
They are comfortable with their own limitations and those of others. They do not have the need to depend on external forces or authorities to give them direction as they are independent. They are capable of forming meaningful relationships and have a deep appreciation for life and its experiences. Some real-life examples of self-actualizing people include Albert Einstein, William James, and Jane Adams. If this need is not met, an individual might feel unsatisfied with their life.
The Extended Hierarchy Of Needs
The original version of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs model had 5 needs, namely, physiological needs, safety needs, belongingness needs, esteem needs and self-actualization needs. Later, Maslow included some extra needs in his model. He added cognitive needs, aesthetic needs and the need for transcendence.
Cognitive needs include the need for knowledge and curiosity.
For example, Stacy has a curiosity to solve really complicated algebra problems. She solves these problems in her free time.
Aesthetic needs include the need to look for beauty and appreciation.
For example, Tiya wants to arrange her wardrobe in a way that looks balanced and pretty.
Transcendence needs include the need for meaning beyond self.
For example, Kim wants to go on a trip to the Himalayas all by himself to explore the place and find some meaning out of it.
Deficiency and Growth Needs
All these above mentioned hierarchies of needs can be classified into 2 types, deficiency needs or lower-order needs and growth needs or higher-order needs. The first four needs come under the deficiency or D-needs and the rest of the top ones come under the growth or B-needs.
The deficiency needs emerge as a result of deprivation. The longer the deficiency needs are denied, the stronger the urge to get fulfil.
For example, Jake has forgotten his water bottle in school today. He had a very hectic day, full of classes and could not drink water for many hours. By the time he reached home, his need for drinking water was extremely strong.
The growth needs, on the other hand, arise from a yearning to be better as a person. These needs continue to remain constant or grow stronger even after being met. An individual may reach a level of self-actualization if the growth needs are completely fulfilled.
For example, Teena is a working professional. She is also an artist and believes that growth and development can happen at any age in life. She recently finished a 12-hour artwork that was widely appreciated. She might have been able to do so, considering her lower-level needs were met satisfactorily.
Research Study
A study by Jon Patton and colleagues analysed the relationship between deficiency needs variables (physiological, safety, love needs) and growth needs variables (academic achievement).
A lot of children experience deficiency needs, hence this study could be helpful in understanding the relationship between these variables to maximise learning outcomes.
Experimentation
The sample for the study consisted of 390 economically limited students from more than 40 schools in the U.S. Deficiency needs were measured by factors derived from parent surveys and growth needs were assessed using factors derived from a parent survey and results from an individually-administered norm-referenced achievement test.
Observation
Parent surveys consisted of 81 items that were answered on a response format of a 4-point Likert scale. The response options for each item ranged from strongly agree to strongly disagree. The results showed a positive relationship between deficiency needs and growth needs.
Health and dental care (Which is a safety need) was found to be the factor that is most significantly related to achievement outcomes (which is a growth need).
Result
This study provides evidence for Maslow’s theory in the sense that academic progress (growth need) can be achieved through improvement in deficiency needs such as safety and belongingness.
Applications of Maslow’s Theory
Maslow’s theory is a very widely used theory for explaining motivation. It can be applied to various walks of life. For example, it can be used at workplaces to take care of and motivate employees. The leader can take care of the employee’s esteem needs by providing rewards for valuable work. The hierarchy of needs is also helpful for self-reflection. We can sit and examine if each of our needs is being met and proceed towards self-actualization.
Another application of Maslow’s theory is meeting physiological needs at the workplace. Having access to proper water and food resources, having a comfortable temperature and a safe restroom is essential for employees to feel comfortable and attain a peace of mind. The safety needs of employees can be taken care of by providing a timely salary, which ensures financial security. It also boosts motivation as employees feel safe.
The need for belongingness can be met in the workplace by providing means for team building activities, an activity lounge, work parties and celebrations, group projects. This could boost motivation for work as well.
Apart from work, this theory can also be applied in other areas of life. If a person is going through a crisis, he or she can ask for help from his family or friends. The belongingness needs will be satisfied and the person will be able to cope in a better way.
Criticism
- There are also certain drawbacks to Maslow’s theory. The main concern is the way he collected data for forming the concept of self-actualization. He used biographies and writings of a few people to conclude his analysis about self-actualization. His data collection could be biased because of his own opinions and the few people do not resemble the whole population so it cannot be generalized to everyone.
- The limitations with this theory lie in the fact that different cultures may cause people to have different hierarchies of needs.
- Most of the people he studied were highly educated white males. He only studied a few females. This error in data collection makes the theory less generalizable to females, illiterates and people from disadvantaged backgrounds.
- Another criticism is that people who do not have their lower needs met can still fulfil their higher needs. For example, Van Gogh, a renowned artist survived in poverty but managed to achieve self-actualization through his art.
- In simple, People necessarily may not satisfy one level after another and may have other needs not mentioned in the list and may be ready to sacrifice some needs.

very nice.Send PPTs .Than q.
constantly i used to read smaller content which as well clear
their motive, and that is also happening with this post which I am reading now.
This is truth.I totally agreed with that hirachy
My sence
Awesome story once again! Thumbs up=)
Aha”i support that fact…..Thumbs up
I like the theory explanation on the hierarchy of communication. actually the results here are just the best. here is the solution on everything you would like to search about communication
This is such a neat summary of Maslow’s Hierarchy! I hope you don’t mind me copying it into my writing about radical hospitality. Let me know!
Please Include the Theory of Hierarchy of Influence of Shoemaker and Reese 1996
Utter tosh. The man was a drug addict like Freud. Why intelligent people would believe anything either postulated is implausible. Their knowledge of what people want, or need, lacked serious research of any real meaning. You might as well believe Dr Spock’s book on how to raise children, which was rubbish. He later admitted he was grossly wrong.
Thank you,
This helped me in oral communication
I like the topic
This is ok but I feel that Love and belonging (Family & Friends) needs should be addressed alongside Physiological needs.
This is great. I would like to copy the image for reference in my eBook. Please let me know if I can do so.
A wonderful day to the creator(s) of this website. I’m an amateur writer and In my new article, I write how developmental models like Maslow’s hierachy of needs changed my life.
I stumbled over the picture in this article and found it the best one for describing the hierarchy of needs.
I was wondering If I could use it for my newsletter post giving credit to this website.
Best,
Max